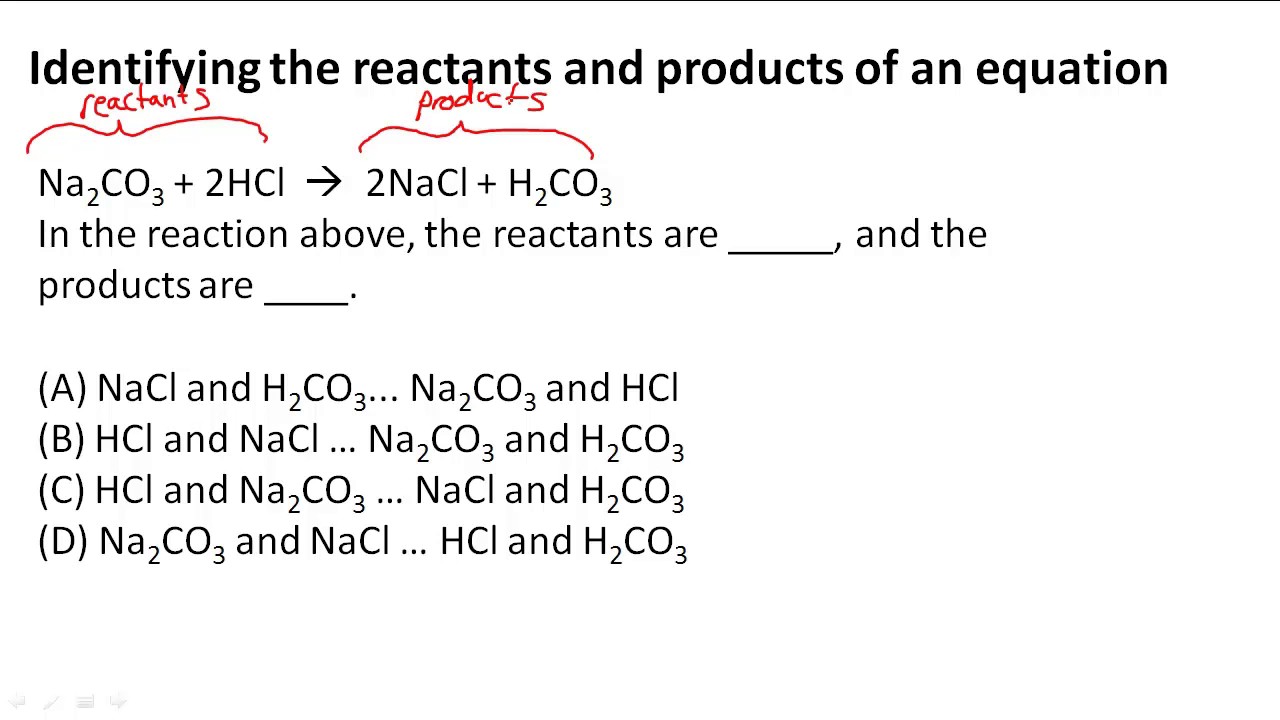
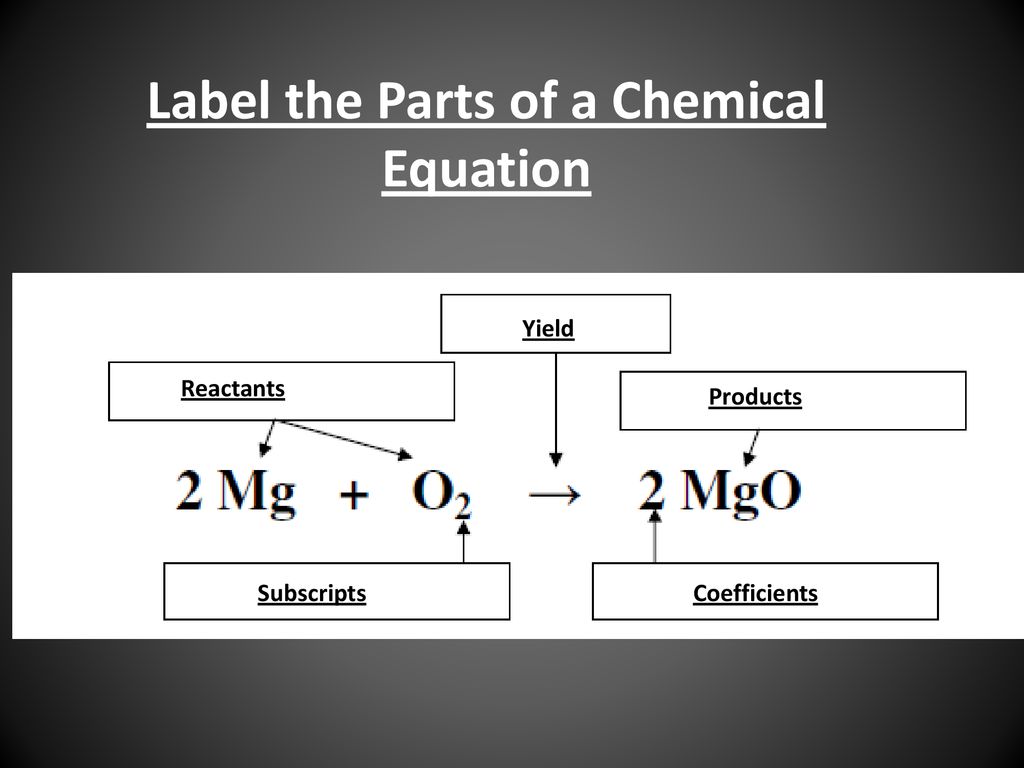
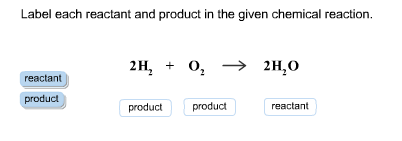
39 label the reactants and products in the chemical reaction
Explosive - Wikipedia An explosion is a type of spontaneous chemical reaction that, once initiated, is driven by both a large exothermic change (great release of heat) and a large positive entropy change (great quantities of gases are released) in going from reactants to products, thereby constituting a thermodynamically favorable process in addition to one that propagates very rapidly. Chemistry Quizzes | Study.com Interested in seeing how well you know a particular chemistry concept? Take Study.com's brief multiple-choice quiz. Obtain rapid feedback and results to understand how well you performed. The quiz ...
H2 + O2 = H2O - Chemical Equation Balancer To balance a chemical equation, enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the Balance button. The balanced equation will appear above. Use uppercase for the first character in the element and lowercase for the second character. Examples: Fe, Au, Co, Br, C, O, N, F. Ionic charges are not yet supported and will be ignored.

Label the reactants and products in the chemical reaction
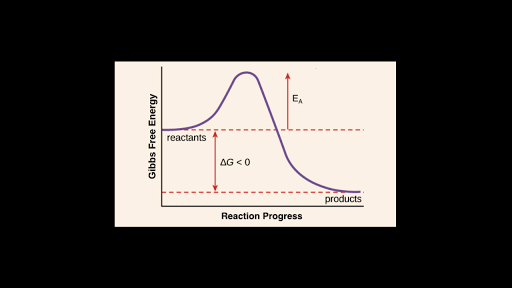
Investigate the Kinetics of the Color Changing Iodine Clock Reaction … Introduction. Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the mechanisms and rates of chemical reactions. The mechanism of a chemical reaction is a description of what happens to each molecule at a very detailed level—which bonds are broken, which new bonds are formed, and how the three-dimensional shapes of the chemicals change during the course … 7.11 Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium - Chemistry LibreTexts Jun 05, 2019 · If ΔG° < 0, then K > 1, and products are favored over reactants at equilibrium. If ΔG° > 0, then K < 1, and reactants are favored over products at equilibrium. If ΔG° = 0, then K = 1, and the amount of products will be roughly equal to the amount of reactants at equilibrium. This is a rare occurrence for chemical reactions. 2.5: Reaction Rate - Chemistry LibreTexts 17/06/2022 · Definition of Reaction Rate. The Reaction Rate for a given chemical reaction is the measure of the change in concentration of the reactants or the change in concentration of the products per unit time. The speed of a chemical reaction may be defined as the change in concentration of a substance divided by the time interval during which this change is observed:
Label the reactants and products in the chemical reaction. Radioactive tracer - Wikipedia A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form … 8.3 Le Chatelier's principle | Chemical equilibrium | Siyavula A decrease in concentration of either the reactants or the products will result in both the forward and reverse reaction rates being lower once equilibrium is re-established. A decrease in reactant concentration will favour the reverse reaction . Chemical reactions - Department of Education and Training Aug 18, 2020 · Changes that may accompany a chemical reaction include colour, appearance and production of new materials, for example, a gas. Mixing alone may not cause a chemical reaction to take place. While heat is often necessary to initiate a chemical reaction it is not always necessary. Chemical reactions are used to produce most of our energy. H2 + Cl2 = HCl - Chemical Equation Balancer To balance a chemical equation, enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the Balance button. The balanced equation will appear above. Use uppercase for the first character in the element and lowercase for the second character. Examples: Fe, Au, Co, Br, C, O, N, F. Ionic charges are not yet supported and will be ignored.
2.5: Reaction Rate - Chemistry LibreTexts 17/06/2022 · Definition of Reaction Rate. The Reaction Rate for a given chemical reaction is the measure of the change in concentration of the reactants or the change in concentration of the products per unit time. The speed of a chemical reaction may be defined as the change in concentration of a substance divided by the time interval during which this change is observed: 7.11 Gibbs Free Energy and Equilibrium - Chemistry LibreTexts Jun 05, 2019 · If ΔG° < 0, then K > 1, and products are favored over reactants at equilibrium. If ΔG° > 0, then K < 1, and reactants are favored over products at equilibrium. If ΔG° = 0, then K = 1, and the amount of products will be roughly equal to the amount of reactants at equilibrium. This is a rare occurrence for chemical reactions. Investigate the Kinetics of the Color Changing Iodine Clock Reaction … Introduction. Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the mechanisms and rates of chemical reactions. The mechanism of a chemical reaction is a description of what happens to each molecule at a very detailed level—which bonds are broken, which new bonds are formed, and how the three-dimensional shapes of the chemicals change during the course …












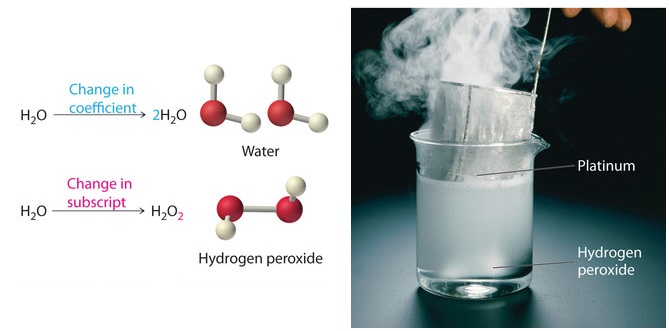






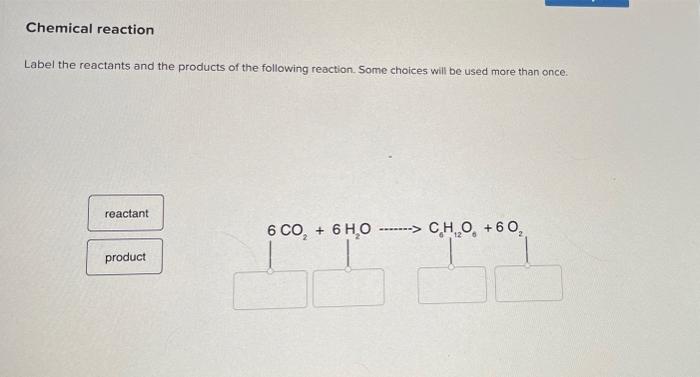
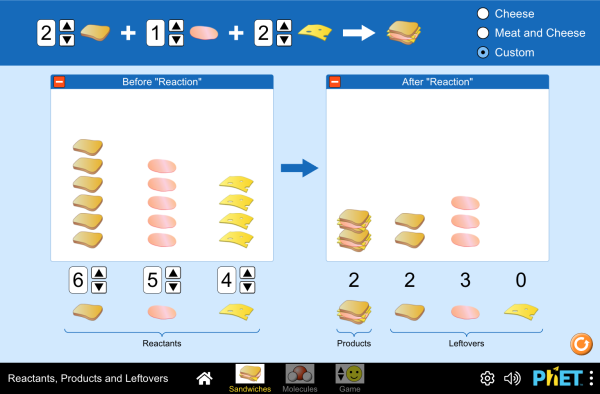
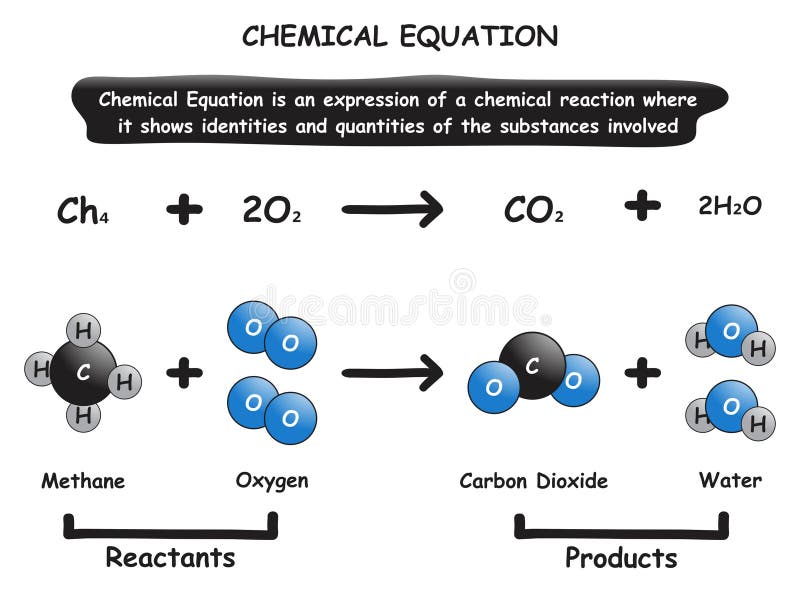


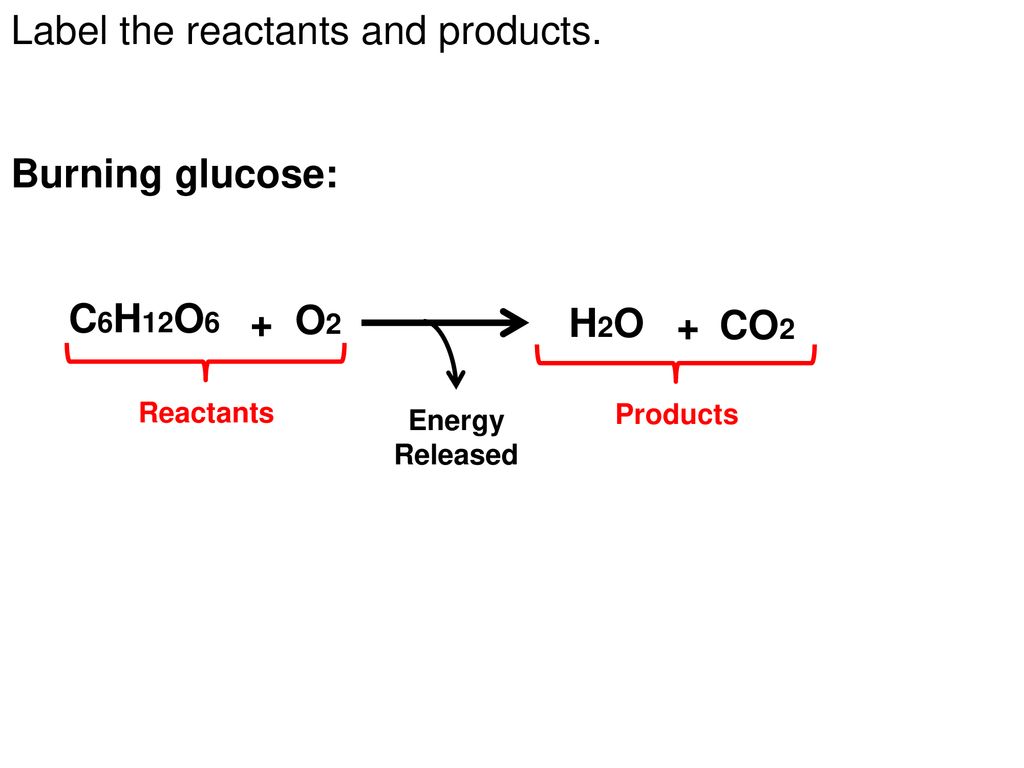




Post a Comment for "39 label the reactants and products in the chemical reaction"